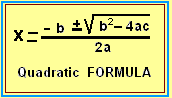
With the variable as x and the a, b, and c the numbers in the quadratic equation
we can find the value for x that will make the above equation true by using this formula:
Solve the equation below. Do you see the right side is 0? One side must be 0. Then we must decide a, b, and c. { a (multiplied by x^2) is 3 and the b (multiplied by x) is -1 and c (the “lone number” is -2}
Do you see that b is -1 so that means -b is +1. Now look under the square root and recall Order of Operation rules. We will get 1 – 12(-2) or 1+24.
Now test your solutions (answers for x). Will the 1 make the quadratic expression above =0? Will the -2/3 also make the above expression =0? They should!